NIST 2.0 Cybersecurity Framework
Why NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
Widely Adopted Standard
Used by over 50% of US organizations and recognized internationally as the leading cybersecurity framework.
Risk-Based Approach
Focuses on business-driven cybersecurity decisions rather than one-size-fits-all compliance requirements.
Flexible Implementation
Adaptable to organizations of any size, industry, or cybersecurity maturity level.
Business Alignment
Directly connects cybersecurity activities to business objectives and risk tolerance.
Understanding the NIST Framework
The CSF 2.0 is organized by six Functions — Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Together, these functions provide a comprehensive view for managing cybersecurity risk.
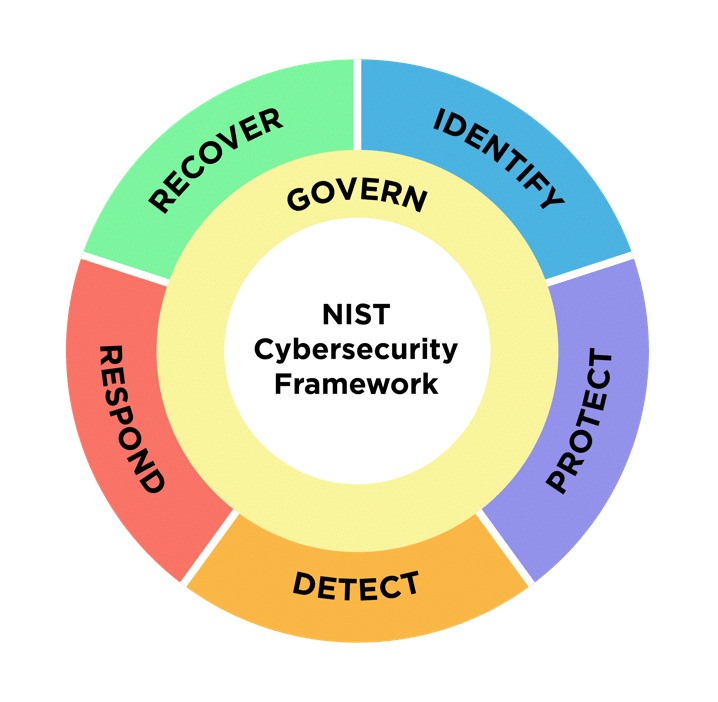
Identify
Understand your cybersecurity risks to systems, assets, data, and capabilities through asset management, risk assessment, and governance activities.
Protect
Detect
Respond
Recover
Govern
Key Benefits of NIST Framework Adoption
Common Language
Provides standardized terminology that facilitates communication between technical teams, management, and external stakeholders.
Cost-Effective Risk Management
Prioritizes cybersecurity investments based on risk assessment rather than compliance checklists or vendor recommendations.
Regulatory Alignment
Supports compliance with various industry regulations and standards without being prescriptive about specific technologies.
Scalable Implementation
Grows with your organization from basic cybersecurity hygiene to advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
Integration Friendly
Complements existing cybersecurity programs and risk management processes rather than replacing them entirely.
Framework Components Explained
Implementation Tiers
- Tier 1 – Partial: Limited awareness of cybersecurity risk with ad hoc risk management practices
- Tier 2 – Risk Informed: Risk management practices approved by management but not established as organizational policy
- Tier 3 – Repeatable: Formal policies and procedures with regular review and organization-wide risk management approach
- Tier 4 – Adaptive: Advanced practices that adapt based on lessons learned and predictive indicators from cybersecurity activities
Core Categories
The framework includes 23 categories across the six functions, each containing multiple subcategories that define specific cybersecurity outcomes. These categories cover areas such as:
- Asset Management and Business Environment
- Governance and Risk Management Strategy
- Identity Management and Access Control
- Data Security and Information Protection
- Anomaly Detection and Security Monitoring
- Incident Response and Recovery Planning
- Supply Chain Risk Management
- Cybersecurity Workforce Development
Profile Development
Profiles help organizations align cybersecurity activities with business requirements by selecting relevant categories and subcategories based on:
- Industry sector and regulatory requirements
- Organizational size and complexity
- Risk tolerance and business objectives
- Available resources and capabilities
- Threat landscape and business environment